

General Description
Polymer Modified bitumen (PMB) is one of the specially designed and engineered bitumen grades that are used in making pavement, roads for heavy-duty traffic, and home roofing solutions to withstand extreme weather conditions. This material is also used as a sealant in residential roofing applications.
consists of bitumen blended with a synthetic polymer or crumb rubber. PMBs are used to enhance the performance of binders on heavily trafficked or distressed pavement surfaces, often in adverse climatic conditions. Property improvements include reduced temperature susceptibility, increased elasticity or resilience, increased cohesion, and improved tenacity once a bond has been established. as a valued engineering material continues to increase. The interest in the modification of bitumen using polymers, whether virgin, scrap, or polymer blends, is intense.
Production of hot asphalt mixes with Polymer modified Bitumen (PMB) is mandatory for enhancing the performance of bitumen used in road, runway, and racetrack applications both by improving life expectancy and reducing maintenance levels.
There are 4 important issues for good quality PMB:
Bitumen quality, polymer compatibility (the most used polymer is SBS), mill performance (a high-quality mill with high power is fundamental to grant the perfect blending of polymer and bitumen), and good agitation of the final product (which is guaranteed by two agitators in each tank).
However, it is brittle in cold environments and softens readily in warm environments. One of the many methods employed to toughen bitumen is to blend it with polymers, either virgin or scrap, to produce (PMB) . A lowering of the breaking point (DIN 52 012) and an increase in ductility (DIN 52 013) by polymer additive show better cold flexibility and are called polymer modified bitumen.
Composition of Polymer Asphalts
Composition of polymer modified bitumen is bitumen plus polymer and a compatibilizing agent prepared by reacting one or more unsaturated monomers with a bituminous composition comprising asphaltenes or resins.
Asphaltenes and resins are two of four broad component groups found in bitumen (the others are aromatics and saturates; resins, aromatics, and saturates are collectively known as maltenes). Asphaltites are n-heptane insoluble black or brown amorphous solids and are generally considered to be highly polar and complex aromatic materials of fairly high molecular weight.
Resins are soluble in n-heptane and are typically dark brown in color, solid or semi-solid, and polar. In one embodiment of the invention, the bituminous composition comprising asphaltenes and/or resins is a bituminous composition comprising all four components, i.e. resins, aromatics, saturates and asphaltenes.
If you are more interested in product information or need to place an order contact or inquire about our Sales team.
PMB Production Process
Manufacturing of PMB starts with preparation of the raw materials. Bitumen is heated up to 170-180° C in service tanks; pre-weighed polymer bags are placed near the feeding screw as per the production specification.
Bitumen is pumped into weighing and mixing tanks, and the polymer is added using metering systems. The operator ensures the polymer is fully loaded, and the PLC control system verifies the bitumen and polymer quantities before mixing. The polymer-bitumen mixture is pumped through a high shear mill to ensure thorough disintegration for quality modification. A 160 kW high shear mill is recommended for high-quality PMB.
During production, one tank is filled while another is processed, thus allowing for continuous operation controlled by PLC.
Storage: PMB blends are stored in special agitation tanks at 160-180°C. Stirring is periodically performed to avoid polymer agglomeration and maintain blend stability. During asphalt production, PMB must be stirred or recirculated to ensure proper mixing.
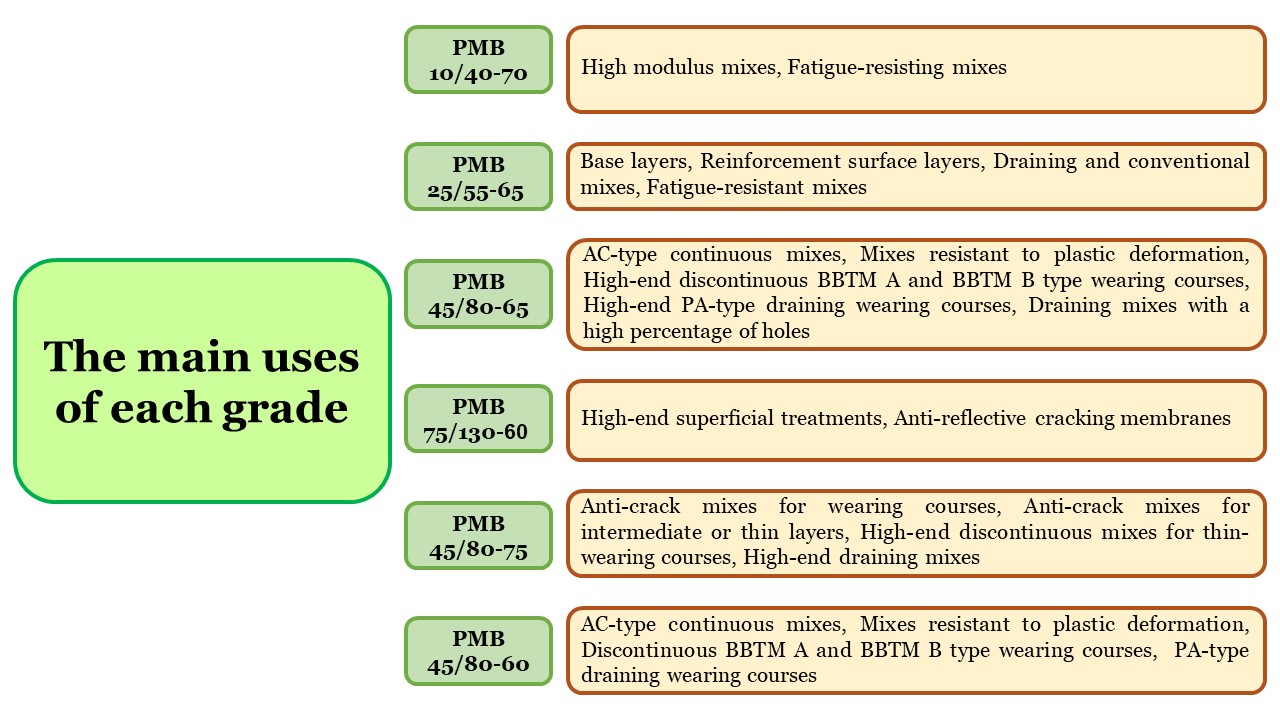
Application of Polymer Modified Bitumen
Polymer Modified Bitumen can be used in asphalt mix designs which results in the manufacture of cohesive asphalt mix with good elasticity suitable for type of traffic. Special attention to be taken to the temperatures while manufacturing, lying and compaction are performed.
- Higher rigidity
- Increased resistance to deformation
- Increased resistance to cracks and stripping
- Better water resistance properties
- High durability
Specification of Polymer Modified Bitumen (PMB)
| Property | Units | PMB 10/40-70 | PMB 25/55-65 | PMB 45/80-60 | PMB 45/80-65 | PMB 45/80-75 | PMB 75/130-60 | Test Method UNE-EN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration @25°C | 0.1mm | 10-40 | 25-55 | 25-55 | 45-80 | 45-80 | 75-130 | 1426 |
| Softening point | °C | ≥ 70 | ≥ 65 | ≥ 60 | ≥ 65 | ≥ 75 | ≥ 60 | 1427 |
| Cohesion. Strength-ductility | J/cm2 | ≥ 2 a 15ºC | ≥ 2 a 15ºC | ≥ 2 a 15ºC | ≥ 2 a 15ºC | ≥ 2 a 15ºC | ≥ 2 a 15ºC | 13589 13703 |
| Fraass breaking point | °C | ≤ -5 | ≤ -7 | ≤ -12 | ≤ -15 | ≤ -15 | ≤ -15 | 12593 |
| Elastic recovery at 25ºC | % | TBR | ≥ 50 | ≥ 50 | ≥ 70 | ≥ 80 | ≥ 60 | 13398 |
| Stability in storage Difference in softening point | °C | ≤ 5 | ≤ 5 | ≤ 5 | ≤ 5 | ≤ 5 | ≤ 5 | 13399 1427 |
| Stability in storage Difference in penetration poin | 0.1mm | ≤ 9 | ≤ 9 | ≤ 9 | ≤ 9 | ≤ 13 | ≤ 13 | 13399 1426 |
| Flash point | °C | ≥ 235 | ≥ 235 | ≥ 235 | ≥ 235 | ≥ 235 | ≥ 220 | ISO 2592 |
| Resistance to Hardening @163°C | ||||||||
| Change of mass | % | ≤ 0.8 | ≤ 0.8 | ≤ 1.0 | ≤ 1.0 | ≤ 1.0 | ≤ 1.0 | 12607-1 |
| Retained penetration | % | ≥ 60 | ≥ 60 | ≥ 60 | ≥ 60 | ≥ 60 | ≥ 60 | 1426 |
| Increase in softening point | °C | ≤ 8 | ≤ 8 | ≤ 10 | ≤ 10 | ≤ 10 | ≤ 10 | 1427 |
| Decrease in softening point | °C | ≤ 5 | ≤ 5 | ≤ 5 | ≤ 5 | ≤ 5 | ≤ 5 | 1427 |
Polymer Modified Bitumen Technical Datasheet
| Designation | PMB 40 | PMB 70 | PMB 120 | Test Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration at 25 ֯C, 1/10mm, 100g, 5 sec | 30-50 | 50-90 | 90-150 | ASTM D5 |
| Softening Point, (R&B), ֯C, Min | 60 | 55 | 50 | ASTM D36 |
| Elastic Recovery at 15 ֯C ,%, Min | 60 | 60 | 60 | ASTM D6084 |
| Flash point , COC, ֯C , Min | 220 | 220 | 220 | ASTM D92 |
| Separation, Difference in Softening Point,(R&B), ֯C, Max | 3 | 3 | 3 | – |
| Thin Film Oven Test & Test on Residue | ||||
| Loss in Mass, %, Max | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ASTM D1754 |
| Reduction in Penetration of residue at 25 ֯C , 100g, 5s, %,Max | 35 | 35 | 35 | ASTM D5 |
| Increase in Softening Point, ֯C, Max | 5 | 6 | 7 | ASTM D36 |
| Elastic Recovery at 25 ֯C, %, Min | 50 | 50 | 50 | ASTM D6085 |
