
General Definition
Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen (CRMB) is made by the amalgamation of crumb rubber modifier and the chosen bitumen grade. The modifier works as an agent that strengthens the binder from the occurrence of any deformation when trying to maintain during low temperature, fatigue or thermal issues.
CRMB is beneficial as it increases the life of a road by 1.5 to 2 times as to using a normal bitumen modifier.
Crumb Rubber is a worldwide newly developed economic solution enhancing the quality of bitumen used in asphalt mixers for road developments.
(CRMB) is designed to maximize resistance to permanent deformation and to reduce fatigue of asphalt mixtures that are used in most locations.
CRMB provides some unique properties different from bitumen binders like the strong adhesion reduces cracking, deformation, etc. It increases the stability of the material, homogeneity throughout the supply chain.
So, it is very necessary to change Bitumen roads to CRMB for higher resistance, smooth drive, comfort and safety.
Types of Crumb Rubber Modified Bitumen
- CRMB 60 => Recommended for warm climate
- CRMB 55 => Recommended for moderate climate
- CRMB 50 => Recommended for cold climate
steps of produce crumb rubber modified bitumen
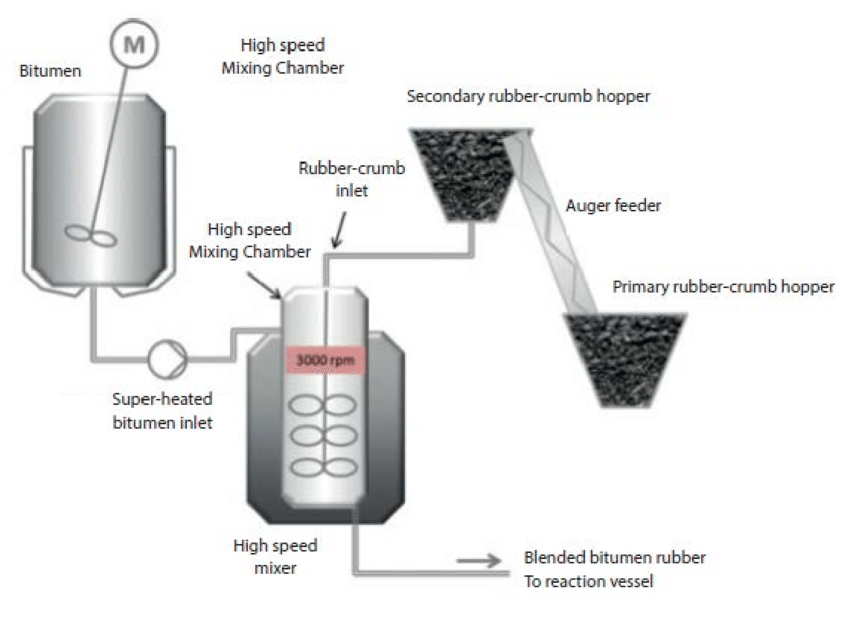
The addition of the correct amount of extender oil to the bitumen is normally done at the refinery. Prior to a batch of bitumen rubber being blended, the bitumen is heated to ± 210°C before the rubber crumb is uniformly added using technologically advanced high speed homogeneous mix blender systems. The operator digitally controls the feed of raw materials in precise proportions.
Once mixed, it is left for at the reaction temperature for a minimum of 45 minutes prior to application. The complex nature of the blend of hydrocarbons, oils and gels means that its viscosity changes significantly over time at elevated temperatures. Bitumen rubber has a limited shelf-life and is typically blended close to where it will be used or applied.
Advantages of Crumb rubber Modified Bitumen
The advantages of using (CRMB) are well documented worldwide, the major drivers for its use being increased fatigue resistance and reduction in ageing of the binder.
Increased focus on the influence of the construction industry on the environment and ways to reduce and re-use waste material have also motivated the use of crumb rubber modified bitumen.
Application of Crumb rubber Modified Bitumen
- Stability & Resistance from extreme weather Conditions.
- Dressing up strong road construction & Development for movement of Heavy Vehicle Movement &
- High Volume of Traffic.
- Parking places
- Bridges and flyovers
- Procuring From low & High Temperature Cracking of roads.
- For Making High Load Highways, Junctions, Sea Port, Runway of AirField, Heavy Traffic
- Movement Roads, etc.
Choosing the Right Crumb rubber modified bitumen:
It has to be kept in mind that CRMB is not a single product. The selection of appropriate CRMB grade depends on various factors, such as:
Volume of Traffic: The volume of traffic that the road or surface is expected to bear decides the selection of the CRMB grade. Higher volumes of traffic require a CRMB that is more resistant to fatigue cracking.
Climate: It is the prevalent climatic conditions, especially extremes in temperature, that determine the kind of CRMB selected. In cold climates, one may require CRMB grades that exhibit flexibility at lower temperatures while hotter climates require more resistance to softening grades.
Project Requirements: Other specific project requirements like noise reduction or considerations of skid resistance also influence the choice of CRMB grade.
Consulting with a qualified engineer or construction professional is highly important in order to select the most suitable CRMB product for your particular project needs.
Packing of (CRMB)
– 180 Kg New Still Drum
Specification
| PROPERTIES | CRMB 50 | CRMB 55 | CRMB 60 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration at 25 ֯C, 1/10mm, 100g, 5 sec | < 70 | < 60 | <50 |
| Softening Point, (R&B), ֯C, Min | 50 | 55 | 60 |
| Elastic Recovery at 15 ֯C ,%, Min | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Flash point , COC, ֯C , Min | 220 | 220 | 220 |
| Separation, Difference in Softening Point,(R&B), ֯C, Max | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Viscosity at 150 ֯C, Poises | 1-3 | 2-6 | 3-9 |
| Thin Film Oven Test & Test on Residue | _____ | _____ | _____ |
| Loss in Mass, %, Max | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Reduction in Penetration of residue at 25 ֯C , 100g, 5s, %,Max | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Increase in Softening Point, ֯C, Max | 7 | 6 | 5 |
| Elastic Recovery at 25 ֯C, %, Min | 35 | 35 | 35 |

