Description of PG Bitumen
Performance Grade (PG) bitumen is a type of asphalt binder that is graded based on its performance in extreme hot and cold temperatures. The PG Bitumen system aims to ensure that the binder has the appropriate properties for the environmental situation it will be used in. It uses tests to measure the physical properties of the binder, which are directly related to field performance in the paving situation. The Long-Term Pavement Performance (LTPP) provides a controlled algorithm to calculate and derive the pavement temperature based on the air temperature above. This helps in selecting the bitumen that performs best in the defined conditions.
Penetration grading and viscosity grading have limitations in characterizing asphalt binder for use in Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) pavement. As part of Super pave research, new specifications and binder tests were developed to more accurately and comprehensively determine the characteristics of asphalt binders for use in HMA pavements. These tests and specifications are designed to address HMA pavement performance parameters such as fatigue cracking, rutting, and thermal cracking.
The PG Bitumen system is defined by two numbers representing pavement temperatures: the highest (PG 64-XX) and the lowest (PG XX-22). These numbers are derived from air temperatures using an algorithm included in the LTPP Bind program.
Super pave performance grading uses the following asphalt binder tests:
- Rolling thin film oven (RTFO)
- Pressure aging vessel (PAV)
- Rotational viscometer (RV)
- Dynamic shear rheometer (DSR)
- Bending beam rheometer (BBR)
- Direct tension tester (DTT)
Performance Grade Bitumen (PG Bitumen) Application
PG52-28 is primarily used for paving in new constructions and maintenance of roads, both. It can be applied to dense-graded and open-graded HMA. This product can also be used in sealing pavement cracks and cracks along the edges. Other uses include spray applications on bridge decks and fabric protective membrane coating in pavements.
PG52-28 is primarily used for paving in new constructions and maintenance of roads, both. It can be applied to dense-graded and open-graded HMA. This product can also be used in sealing pavement cracks and cracks along the edges. Other uses include spray applications on bridge decks and fabric protective membrane coating in pavements.
PG 58-22 is used principally for paving in dense-graded and open-graded HMA and for road construction. It can also be applied for spraying and crack-sealing applications. This type of grade is especially preferred for very cold regions.
PG58-34 is widely used in highways at high elevations. This type of paving asphalt cement is mainly used in manufacturing Hot Mix Asphalt, or HMA. It is also suitable for sealing the edges between new and old pavements and for crack sealing.
PG58-40 is best applied in high-elevation areas. This type of paving asphalt can be used in the production of Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA), which is particularly good for sealing and crack treatment.
PG64-22 is commonly applied in a lot of the paving of new construction and pavement treatments. It has a good performance in both dense-graded and open-graded Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) usages. This grade is good to go for sealing and crack treatment as well. Other uses include tacking applications on bridge decks and pavement protective layers using fabrics. Of special importance is the fact that, with appropriate aggregate selection and asphalt content, HMA made with PG 64-22 as the binder can be less tender than mixtures with softer asphalt. Thus, mixture shoving, checking when the pavement surface is scuffed, and rolling or markings due to traffic soon after laying may be significantly reduced.
PG64-28 is primarily utilized in road construction and paving for both new projects and pavement maintenance. It is effective for dense-graded and open-graded HMA applications. Other uses include spray applications on bridge decks and pavement protective layers with fabrics. PG64-28 is commonly used in low-elevation areas.
PG70-22 is a high-volume traffic volume area pave. This type of paving asphalt cement is generally used in HMA production that can be good for pavement edge sealing and crack sealing.
Which PG asphalt should perform best in resisting thermal cracking?
- PG 64 -22
- PG 76 -22
- PG 64 -28
- PG 58 -34
Which of the following PG binders should perform best in resisting rutting?
- PG 82 -22
- PG 76 -28
- PG 70 -28
- PG 76 -22
Effect of Traffic Speed and Volume on Binder Selection
Examples:
- Base Grade PG 58 -22
- For toll road – (high Volume) PG 64-22
- For toll booth – (high volume and slow traffic) PG 70-22
- For rest area – (high volume and standing traffic) PG 76-22
|
Out of the numerous Performance Grade(PG) bitumen available in the market, Performance Grade Bitumen 64-22 is one of the top-grade and highest-selling products internationally. |
PG Bitumen 76-22 is a high-performance paving-grade asphalt binder classified in the Performance Grade system. It operates under extreme temperatures and consistently exhibits its performance, |
PG Bitumen 58-16 is a category of bituminous binder assigned according to the Performance Grade System. The performance-grade classification of asphalt provides conformance-based categorization that may be... |
Understanding the PG Grade System
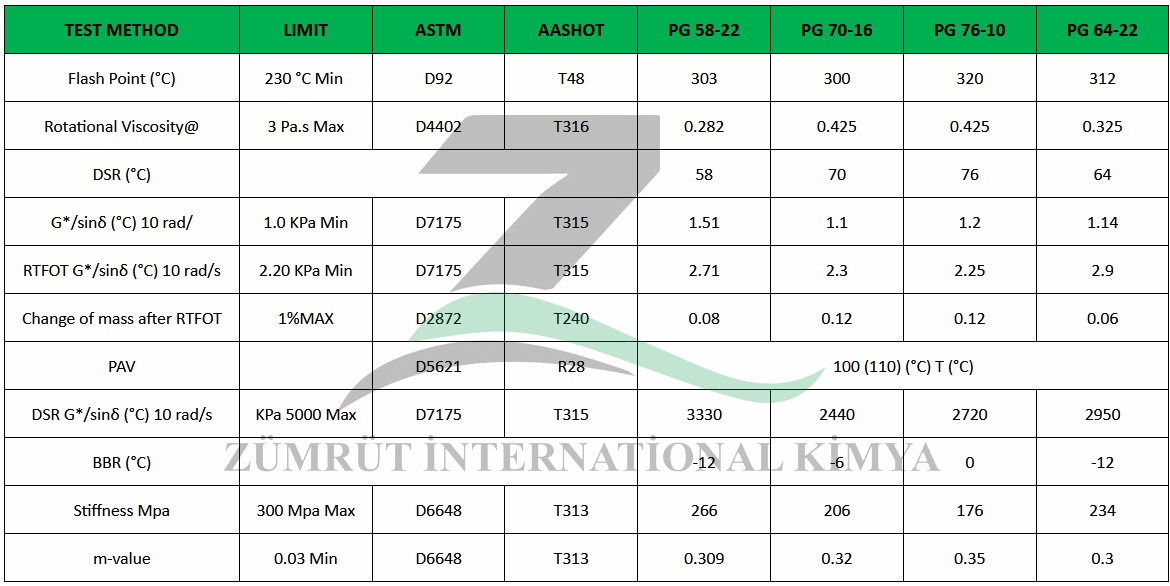
The PG Bitumen system is based on climate and consists of two portions: high and low pavement service temperature. High temperature performance is concerned with rutting, which takes time to cumulate, and the average 7-day maximum pavement temperature is used for high temperature climates. Low temperature climates are concerned with thermal cracking during cold nights, and the minimum pavement temperature is used for low temperature climates. PG Bitumen are graded in 6°C increments, with the average 7-day maximum pavement temperature typically ranging from 46 to 82°C and the minimum pavement temperature typically ranging from −46°C to −10°C.
A binder identified as PG 64-10 must meet performance criteria at an average 7-day maximum pavement temperature of 64°C and a minimum pavement temperature of -10°C. The maximum pavement temperature is typically higher than the air temperature by about 20°C due to the dark color pavement absorbing heat and retaining it. The common minimum reliability used is 98%, meaning that when selecting PG 64-10 binder, the asphalt binder in AC pavement should perform satisfactorily under normal traffic conditions within the extreme pavement temperature range of -10°C and 64°C throughout its service life with a minimum 98% confidence level.
Polymer modified binders are used for extra performance and durability, especially when good rutting resistance for high temperature and good thermal cracking resistance for low temperature are concurrently required in the same application. To differentiate between polymer modified and unmodified binders, add both low and high temperature grades together.
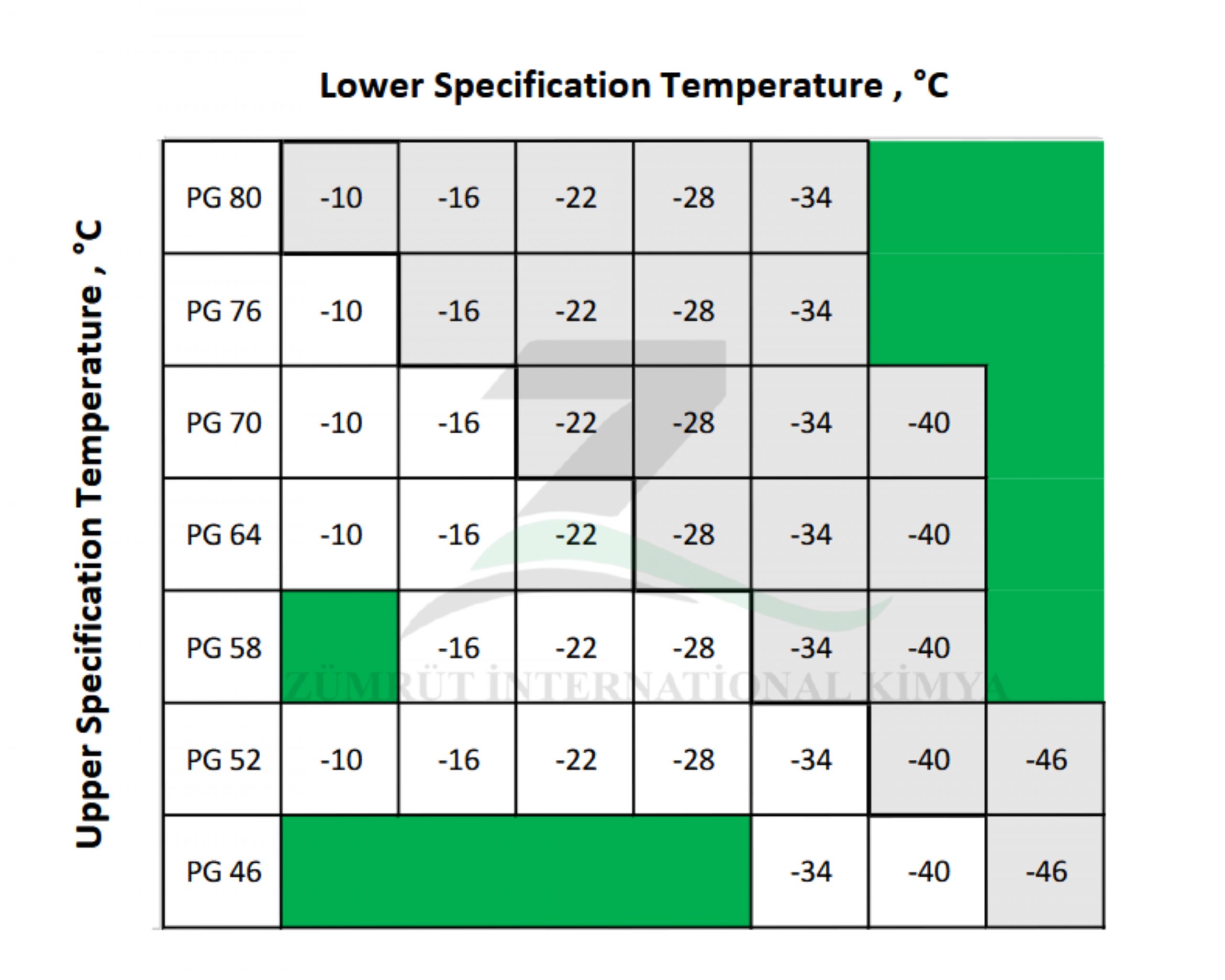
Specification
| Purpose | Specification | Test Method | Property |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ensures proper handling and pumping during production. | ≤ 3 Pa.s at 135°C | ASTM D4402 | Viscosity |
| Resistance to rutting at high temperatures. | ≥ 1.0 kPa (Unaged) at high temperature | AASHTO T315 | Dynamic Shear Modulus (G/sin δ)* |
| Simulates aging during mixing and construction. | - | AASHTO T240 | Rolling Thin Film Oven (RTFO) Residue |
| Ensures rutting resistance after short-term aging. | ≥ 2.2 kPa (RTFO Residue) | AASHTO T315 | G/sin δ (Aged Binder)* |
| Resistance to thermal cracking in cold climates. | ≤ 300 MPa at low temperature | AASHTO T313 | PAV Residue Stiffness (S) |
| Ability to relieve thermal stress in cold climates. | ≥ 0.300 at low temperature | AASHTO T313 | PAV Residue Relaxation (m-value) |
| Ensures durability by limiting volatile loss. | ≤ 1.0% | AASHTO T240 | Mass Loss (RTFO) |
| Safety during handling and storage. | ≥ 230°C | AASHTO T48 | Flash Point |
| Flexibility to resist cracking. | ≥ 50 cm at 25°C | AASHTO T51 | Ductility |
Analysis